Hercules: The Son of Zeus
| Object: | Hercules | ||||||
| Location: | Savoy, MA | ||||||
| Observer: | Roland Roberts | ||||||
| Time: | 2002-Aug-08 23:00 EDT | ||||||
| Camera: | Pentax K1000, 50 mm f/1.4 lens | ||||||
| Camera: | Pentax Spotmatic, 50 mm f/1.4 lens | ||||||
| Film: | Kodak Elite Chrome II, ISO 200 | ||||||
| Exposure: | 30 min @ f/2.8 + 30 min @ f/4 | ||||||
| Processing: |
|
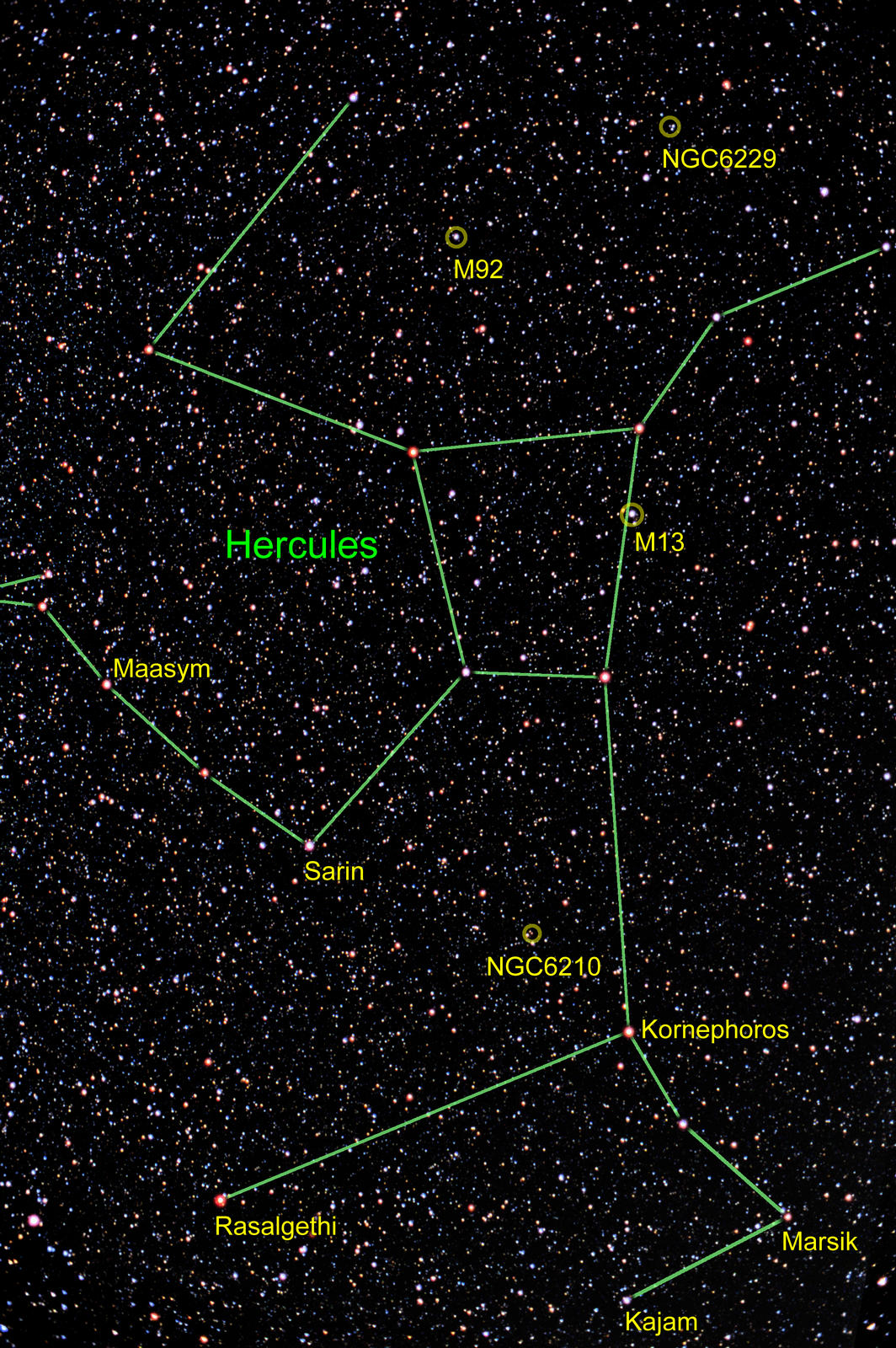
Hercules passes directly overhead on summer nights in the mid-northern latitudes. Still, Hercules possesses none of the extraordinarily bright stars like Lyra or Orion to make it a readily recognizable constellation. The most recognizable feature for locating Hercules in the night sky is the “keystone” shape which forms the body of Hercules.
Hercules enjoys better name recognition than most of the Greek heroes, even among those immortalized in the constellations. In the United States, at least, there is some feedback in keeping him popular from the movie industry, ranging from the 1939 movie Hercules, though the 1990s series “Hercules: The Legendary Journeys,” and even the Disney animation. For general information about the myths surrounding Hercules and more links, have a look at this Russian site.
Interestingly, it would appear that although we know the constellation as Hercules, it was originally known to the Greeks as simply “the Kneeling Man” and the origins of this designation seem to have been lost even to the Greeks.
The following objects are labeled in the image:
- Globular Clusters (3): M13, M92, and NGC 6229.
- Planetary Nebula (1): NGC 6210.
- Stars (6): Kornephoros, Rasalgethi, Sarin, Marsik, Maasym, Kajam.
The planetary nebula NGC 6210 is far too small (0.3″) to resolve at any scale available to most amateurs, but it is incredibly bright. It’s magnitude is nearly the same as M57 in Lyra, but its size means its surface brightness is much higher. In any event, is shows up as a small reddish speck on this image (although unless you are looking at the small version of this image you will not see it).
The globular cluster NGC 6229 is not so close to the edge of visibility in this image, but there two stars about 5 arc-seconds away to the west which makes it difficult to distinguish except at the highest size available here. Of course, none of the globular clusters show any structure at this scale; the film resolution appears to be about 1-3 arc-minutes.
Resources:
Search
.Archives
- October 2024 (1)
- May 2024 (2)
- April 2024 (3)
- September 2022 (5)
- April 2022 (1)
- January 2022 (3)
- December 2021 (4)
- September 2021 (3)
- July 2021 (1)
- January 2021 (1)
- November 2020 (2)
- October 2020 (2)
- September 2020 (2)
- August 2020 (5)
- July 2020 (1)
- November 2019 (2)
- September 2019 (1)
- August 2019 (2)
- September 2017 (1)
- August 2017 (1)
- September 2015 (3)
- August 2015 (2)
- June 2015 (5)
- May 2015 (3)
- May 2013 (2)
- January 2013 (1)
- December 2012 (2)
- September 2012 (1)
- June 2012 (1)
- May 2012 (1)
- October 2011 (2)
- September 2011 (2)
- April 2011 (2)
- March 2011 (10)
- January 2011 (8)
- November 2010 (2)
- October 2010 (1)
- September 2010 (3)
- August 2010 (2)
- July 2010 (1)
- June 2010 (1)
- April 2010 (3)
- February 2010 (3)
- January 2010 (3)
- December 2009 (6)
- November 2009 (3)
- October 2009 (7)
- September 2009 (8)
- August 2009 (4)
- July 2009 (1)
- June 2009 (2)
- May 2009 (2)
- April 2009 (7)
- March 2009 (1)
- February 2009 (6)
- January 2009 (4)
- December 2008 (4)
- November 2008 (3)
- October 2008 (11)
- September 2008 (4)
- August 2008 (5)
- July 2008 (5)
- June 2008 (2)
- April 2008 (4)
- March 2008 (18)
- February 2008 (9)
- November 2007 (1)
- October 2007 (3)
- July 2007 (3)
- April 2007 (1)
- March 2007 (6)
- February 2007 (3)
- December 2006 (3)
- October 2006 (4)
- September 2006 (1)
- July 2006 (5)
- May 2006 (10)
- April 2006 (9)